In the world of text production and analysis, the readability index is a useful tool for evaluating the comprehensibility of a text. Especially in times when more and more emphasis is placed on clear and accessible communication, readability indices play a crucial role. This blog post explains what the readability index is, how it is measured, the different methods available and how these indices support the principles of Plain Language. It also explains the difference between the general readability index and the more specific Flesch index.
Table of contents
ToggleWhat is the readability index?
The readability index, also known as the readability index, is a measure of how easy or difficult a text is to understand. It provides information on how comprehensible a text is for a specific target group by evaluating the linguistic complexity of the text. The index is based on certain linguistic factors, such as the length of sentences, the frequency of long words and the general structure of the text.
How is the readability index calculated?
There are various methods for calculating the readability index, each of which uses different calculation formulas. Some of the best known and most frequently used formulas are
- Flesch-Reading-Ease-Formula (Flesch-Index):
- The Flesch Reading Ease formula was originally developed by Rudolf Flesch and measures the comprehensibility of a text on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher values indicating easier comprehensibility.
- See "Formula for the readability index"
- A score of 90-100 means that the text is very easy to understand and suitable for a wide audience (e.g. children or beginners). A value of 60-70 is considered suitable for the general public. Texts with a value of 30 or less are difficult to understand and are intended for specialist audiences or experts.
- Hohenheim Intelligibility Index (HIX):
- The Hohenheim Index measures the comprehensibility of a text specifically for the German language. Factors such as the proportion of nouns and sentence structure are also included in the calculation.
- Viennese factual text formula:
- This formula is specifically intended for non-fiction texts and uses the average sentence length, word length and the proportion of long words to determine the comprehensibility of a text. It specifies a value between 1 and 20, with a low value indicating high comprehensibility.
Formula for the readability index
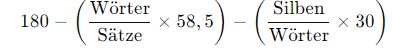
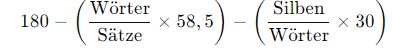
Factors that influence the readability index:
The factors that determine the readability index include the following:
- Sentence length: Long sentences are more difficult to understand than short ones. A text with many short sentences is rated as easier to read.
- Word length: Short, simple words contribute to better readability. Complex, long words or technical terms reduce comprehensibility.
- Number of syllables: The more syllables a word has, the more difficult it is for the reader to grasp the text quickly.
- Structure and grammar: Complicated sentence constructions, many subordinate clauses or passive formulations increase the complexity of the text.
Where can you measure the readability index?
Nowadays, there are numerous tools and software programs that can be used to measure the readability index of texts. Some of the most common methods are:
1. online tools
There are numerous websites that make it possible to enter texts into various readability formulas and immediately assess their comprehensibility. Examples include
- readability-score.comThis tool analyzes texts according to various formulas, including the Flesch Reading Ease formula.
- Hemingway AppThis app highlights complicated sentences and offers suggestions to improve comprehensibility.
2. word processing programs
Programs such as Microsoft Word offer built-in readability checks using the Flesch index. After running the spell check, Word displays the Flesch Reading Ease Score and the Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (for the American school system).
3. SEO tools
Many SEO plugins, such as Yoast SEO, which are used on WordPress websites, analyze the readability of online content and provide feedback to improve comprehensibility.
4. browser plugins
There are also extensions for web browsers that analyze the readability of texts and thus help to directly measure the readability index on websites.
What does the readability index mean?
The readability index provides information on how difficult or easy a text is to understand for a specific target group. Texts with a high readability score are easier to understand and can be grasped by a broad readership. Texts with a low score are complex and require a higher level of education or specialized knowledge in order to be understood.
Interpretation of the results:
- High readability value (e.g. 90-100 for the Flesch Index): Very easy to understand. Suitable for young readers, beginners or a broad target group.
- Medium readability value (e.g. 60-70 for the Flesch Index): Adequate comprehensibility for the general public. This is the optimal range for many texts such as news articles or general content.
- Low readability score (e.g. below 30 on the Flesch Index): Difficult to understand, often suitable for experts, scientific texts or legal documents.
The role of the readability index in plain language
Plain language is a simplified form of standard language that aims to make information understandable for all people, regardless of their linguistic abilities. Simple language follows certain rules, such as short sentences, simple vocabulary and a clear structure, in order to increase comprehensibility.
The readability index is a valuable tool for checking whether a text meets the requirements of Plain Language. Plain language texts should have a high readability score as they use short sentences and easy-to-understand words. The Flesch Reading Ease Index offers a quick way to check whether a text is actually easy to read.
Difference between readability index and Flesch index
The readability index is a generic term for various methods for measuring the readability of a text. It is not a specific formula, but a general category of metrics that can be calculated in different ways depending on the method used (e.g. Flesch index, Hohenheim index or Vienna non-fiction formula).
The Flesch Index, or more precisely the Flesch Reading Ease Index, is a specific formula within the readability index. It is one of the best-known methods for evaluating text comprehensibility and is based on two fundamental variables: the average sentence length and the number of syllables per word.
Summary of the differences:
- Readability index:
- General term for various methods for measuring readability.
- Includes many different formulas, such as the Flesch Index, the Wiener Sachtextformel or the Hohenheim Index.
- Flesch index:
- Specific formula for calculating readability.
- Takes sentence length and syllable count into account to calculate a value on a scale from 0 to 100.
Similarities and differences:
- Both indices measure the comprehensibility of texts, but are based on different calculation formulas.
- The Flesch index is a specialized method that exists within the general concept of the readability index.
Conclusion
The readability index is an indispensable tool for assessing the comprehensibility of a text and ensuring that it is appropriate for the target audience. The Flesch Index is a widely used method, often used in conjunction with Plain Language, to check the readability of texts. Both indices help to make texts more accessible

